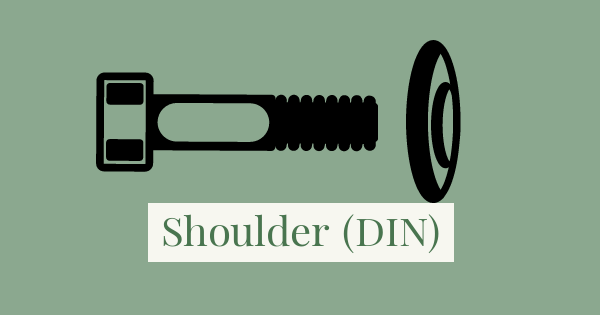
A counterbored hole is usually used for when the top of a screw or bolt needs to be flush with, or sit just beneath, the surface of the material it is inserting.
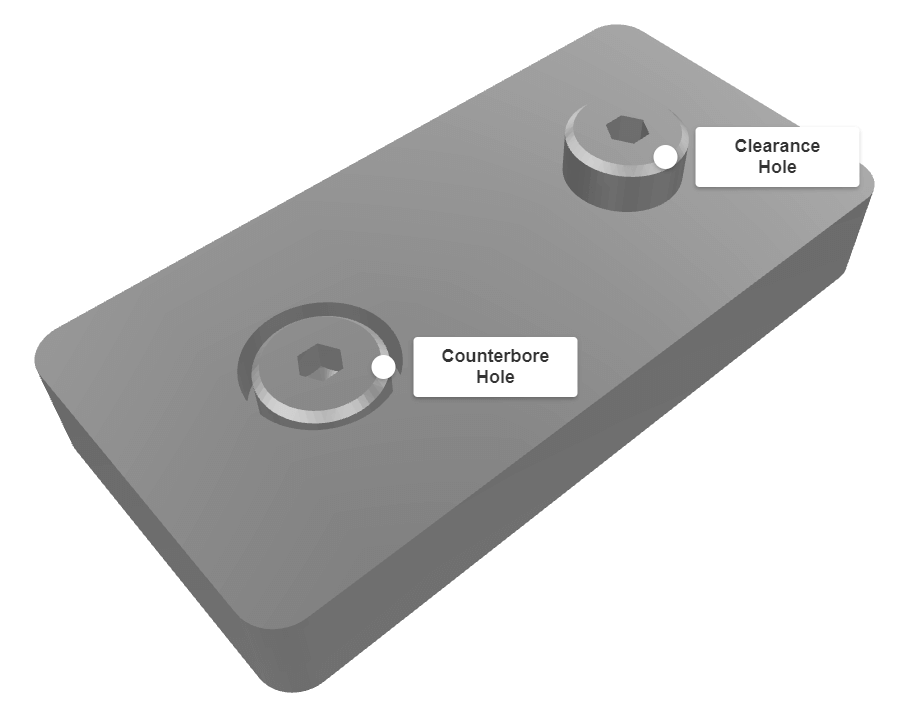
An example of a shoulder screw and the corresponding counterbore hole is shown in this 3D model:
Use the image and chart below to determine what dimensions to use, all dimensions are in millimetres.
For example, a DIN M6 shoulder screw with a normal fit counterbored hole will require a pilot hole diameter of 9 mm, a counterbore diameter of 17 mm, and a counterbore depth of 5.5 mm.
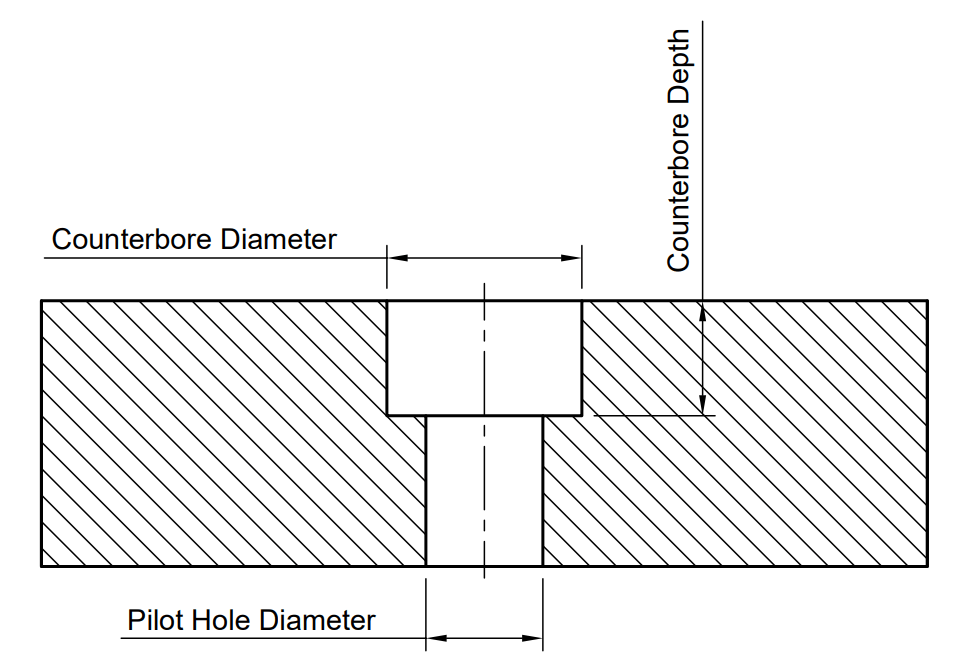
Counterbore Hole Size Chart for Shoulder Screw Fasteners (DIN)
All dimensions are in millimetres.
Fastener Size (Thread) | Pilot Hole Diameter (Close Fit H12) | Pilot Hole Diameter (Normal Fit H13) | Pilot Hole Diameter (Loose Fit H14) | Counterbore Diameter | Counterbore Depth |
| M5 | 7 | 7.4 | 8 | 13 | 4.5 |
| M6 | 8.4 | 9 | 10 | 17 | 5.5 |
| M8 | 10.5 | 11 | 12 | 19 | 7 |
| M10 | 14 | 14.5 | 15 | 23 | 9 |
| M12 | 17 | 17.5 | 18 | 27 | 11 |
| M16 | 21 | 22 | 24 | 35 | 14 |
| M20 | 27 | 29 | 31 | 42 | 16 |
If you want to learn more about counterbored holes, see our post here.