Computer engineers develop, design, test, and repair different types of computer hardware.
As for electrical engineers, they do the same kinds of operations to electronic devices and equipment.
If you are interested in engineering keep reading to review the main differences between both worlds, which will help you decide which one is better for you.
If you have an interest in engineering in general, you should know the differences and most importantly that it is not the same job. Electronics are a part of the computer hardware, yes, but computer engineering is more about the hardware units and their relationships instead of their electrical components.
To acquire a better understanding of both, we should start with a brief overview of the disciplines.
What is Computer Engineering?
Computer Engineering (CoE) integrates several fields of electronic engineering and computer science required to interact with computer software and hardware. It involves building, designing, and fixing computer components.
It is impressive how close both branches are because basically as a computer engineer you will be working with the end products that electrical engineers deliver.
The first thing that people visualize when it comes to computer engineering is building hardware parts and troubleshooting any issues related to the connection between each other. Depending on your set of skills and education you can easily choose which specialisation suits you better.
Let’s take a look at what you need to know to set the right expectations.
What do Computer Engineers do?
As a computer engineer, you will specialise in computer hardware and architecture. Everything from IT communication and security to software development and hardware can be labelled computer engineering.
Some of the major computer hardware components are circuit boards, processors, memory sticks, and cooling solutions.
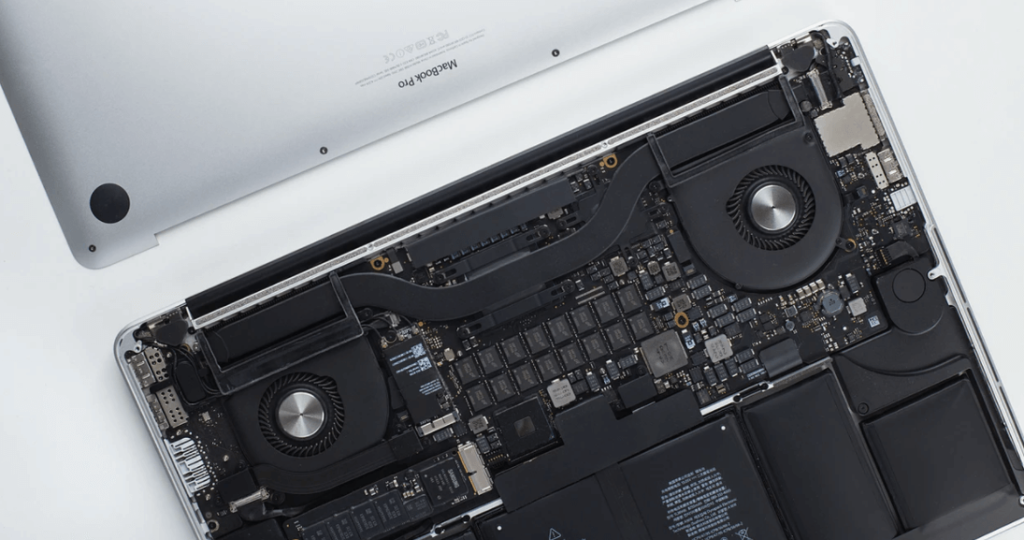
Here is a detailed view of what computer engineers work with:
- CPU – The Central Processing Unit, also called a central processor is the heart of the computer hardware. It is responsible for all mathematical calculations. It only understands information in standard type (binary), executing all input commands including logic, controlling, and arithmetics. Different types of processors are using different slots to connect to the motherboard.
- GPU – Graphics Processing Unit is a circuit board responsible for creating frames (images) for various software. High-end GPUs are used for rendering high-quality videos, games, and graphics. Most of the graphic circuit boards are connected to the motherboard with PCI Express slots which is the main bridge connecting it to all else in computer hardware.
- Motherboard – It is also called the mainboard, this is the main circuit board in computer hardware with the purpose of allowing communication between all electrical components in a computer system. The CPU and GPU, we’ve discussed, are also connected to the motherboard.
- RAM – Random-Access Memory is a digital memory used to store temporary information and software that is currently in use by the user.
- Input & Output Devices – Monitors, mouses, audio devices, controllers, microphones, and more.
- Network Components – Switches, routers, modems, and adapters.
These are just the main aspects that you will be working on as a computer engineer if you are specialising in hardware.
Keep in mind that computer engineers could be also programmers, IT administrators, or developers where the field of work is oriented around the software.
What is Electrical Engineering?
Electrical engineering involves the conversion, transmission, and generation of electric energy. Furthermore, it contains anything with electronic circuits including, flexible circuits, Rigid circuits, and their components.
As one of the new branches of engineering, it is dealing with the technology of electricity.
What do Electrical Engineers do?
Electrical engineers are working on a wide range of electronic components, microchips, and different devices linked together they have one priority.
As an electrical engineer, you will develop, test, and design the manufacturing of electrical components and equipment including radars, navigation systems, motors, and communication systems.
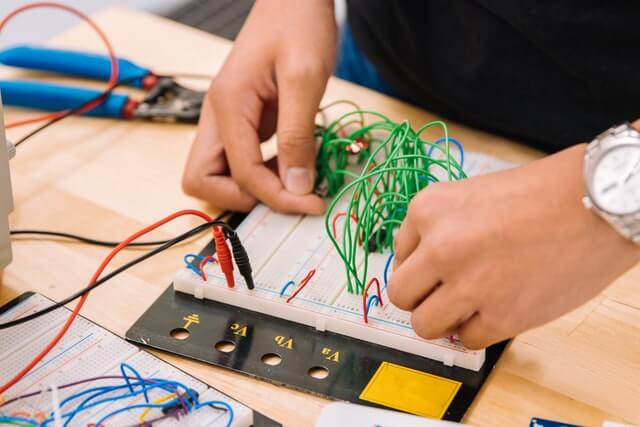
Unfortunately, we cannot list down every single aspect of being an electrical engineer because electrical components are found in every single piece of technology that surrounds us in our daily lives. Depending on where you’re working your field of work and duties may be different than other electrical engineers.
Nowadays, electrical engineers are building devices using some of the most common and basic electronic components such as magnets, batteries, resistors, switches, inductors, capacitors, diodes, transistors, and coils.
The skill-set that you will need in order to start working as an electrical engineer includes an understanding of electronic history, mathematics, and design. All these skills contribute to the end design of circuits that will perform specific operations in a certain electronic device.
We can’t possibly cover everything that an electrical engineer can do, instead, we will review just one industry requiring electrical engineers as employees. Here is a process of designing a Printed Circuit Board (PCB) that will provide you with a clear vision of what you can expect if you are in this field of work:
1. Inserting Solder Paste
Extreme precision is required for this process, as solder paste needs to be applied to those areas of the printed circuit board where the components pads are. To achieve such an insertion, engineers use a solder screen runner that is squeezing solder paste while moving across the screen through holes premade on the board. The amount of solder has to be exact and the whole process is done in a controlled environment.
2. Component Mounting – Pick & Place
The pick and place process can begin only after the solder paste is inserted on the board. During this stage, a machine equipped with all the components is placing them at their right spots on the printed circuit board. The tension of the solder paste is keeping the components in place. Every printed circuit board has its own design information that is later provided to the pick and place machine, which executes with extreme precision.
During other assembly processes, for example, the pick and place machine is squirting a very small amount of glue to secure the position of the components, but this is only done whenever the board is to be wave soldered. The method with the glue is not preferred over the traditional way due to the difficulties that may occur in case of requested repair, even though the glue should degrade during the soldering process.
3. Soldering
Now, when the components are added to the board, the next step of the assembly is the production process on the soldering machine. The wave assembly processes do not pass through the soldering machine, this process is not preferred for surface mount components. However, in these cases, the solder is provided by the wave soldering machine, but reflow soldering is the method that most electronic engineers go with these days.
4. Inspection
After the soldering process, high-end manufacturers always pass their board for inspection. However, manual inspection is not a reliable way for the surface mount boards, instead, an automatic optical inspection is performed, in which there is much more clarity in the micro-level of possible failures. The machines that are executing the inspection stage are designed to locate faulty components, bad soldering, and any perspective for malfunctioning.
5. Test
This is one of the most important objectives in the process. It is extremely important for the PCB manufacturers to test their entities after the electronic assembly process. There are a series of durability and stress tests before a PCB can exit the assembly process. Quality and reliability are mandatory when it comes to PCB assembly due to the damage that a faulty PCB can cause to a certain industry.
6. Feedback
During and after the process of electronic assembly the input and output of the printed circuit board are monitored in order to ensure the rightful execution of its duties. Many failures and malfunctions are detected via this method and the issues are resolved in the early stages which are preventing further complications.
The perfect place for a feedback test is right after the soldering process because this is the part in which most of the issues are occurring. This way the defect is detected quickly and resolved before the next step of the assembly process.
Keep in mind that these steps of building circuit boards are just one of the different industries. Electrical engineers can also participate in the maintenance of electrical control systems as well as interacting with the machinery and equipment.
Many of them work in transport, lighting, ventilation, and networking in manufacturing companies. If you want to become an electrical engineer keep in mind that mathematics is essential. You will also need to have a good understanding of physics and chemistry to a certain degree.
The demand for electrical engineers is growing all around the world and university requirements are different everywhere. You can check the best universities for engineering degrees.

Bottom Line
Now when you know what electrical and computer engineering is, you can easily decide which suits you better. If you have read the whole article, then you have a clear understanding of the differences between both branches and you will never mistake them again.
Related Content:
35 Best Books for Engineers (That Aren’t Textbooks)
23 Engineering Tools You Should Know About (Physical Tools)
Now We’d Like to Hear From You
There you have it: Computer engineering vs electrical engineering.
Now we’d like to hear what you have to say:
Are you interested in becoming a computer engineer or an electrical engineer?
Or maybe you already are one of these types of engineers?
Either way, let us know by leaving a quick comment below.

