A countersunk hole is used for flat head fasteners which have a flat top face and then a taper down from the top face.
They are used when the top of a screw or bolt needs to be flush with the surface of the material it is inserting.
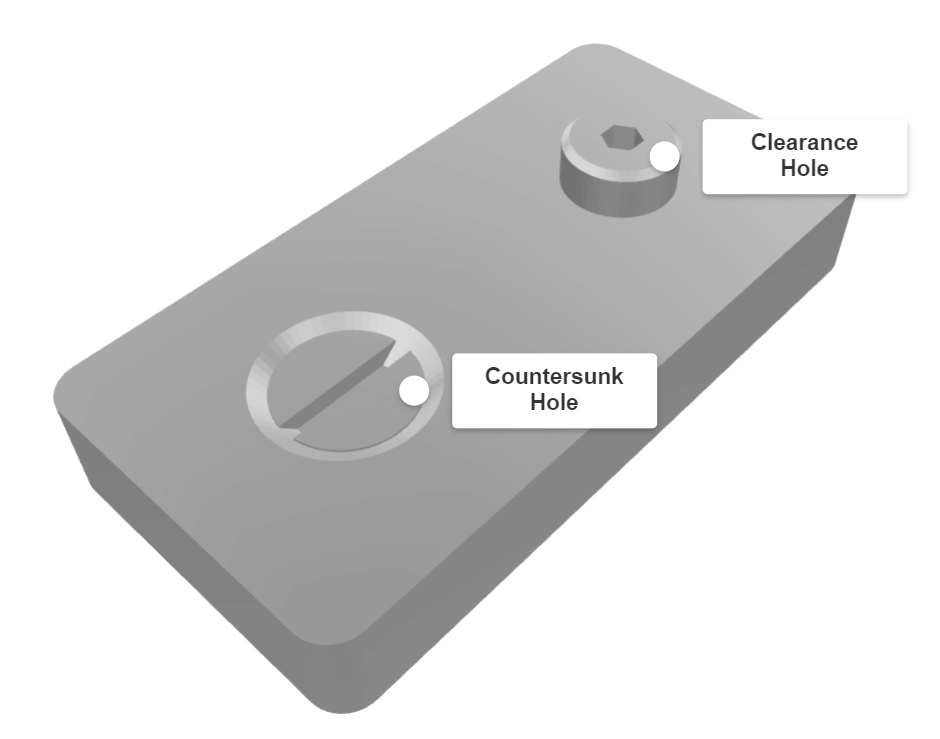
An example of a flat head screw and the corresponding countersunk hole is shown in this 3D model:
Use the image and chart below to determine what dimensions to use, all dimensions are in millimetres apart from the countersink angle.
For example, an ANSI Metric M4 machine screw with a normal fit countersunk hole will require a pilot hole diameter of 4.5 mm, a countersunk diameter of 9.4 mm, and a countersunk angle of 90°.
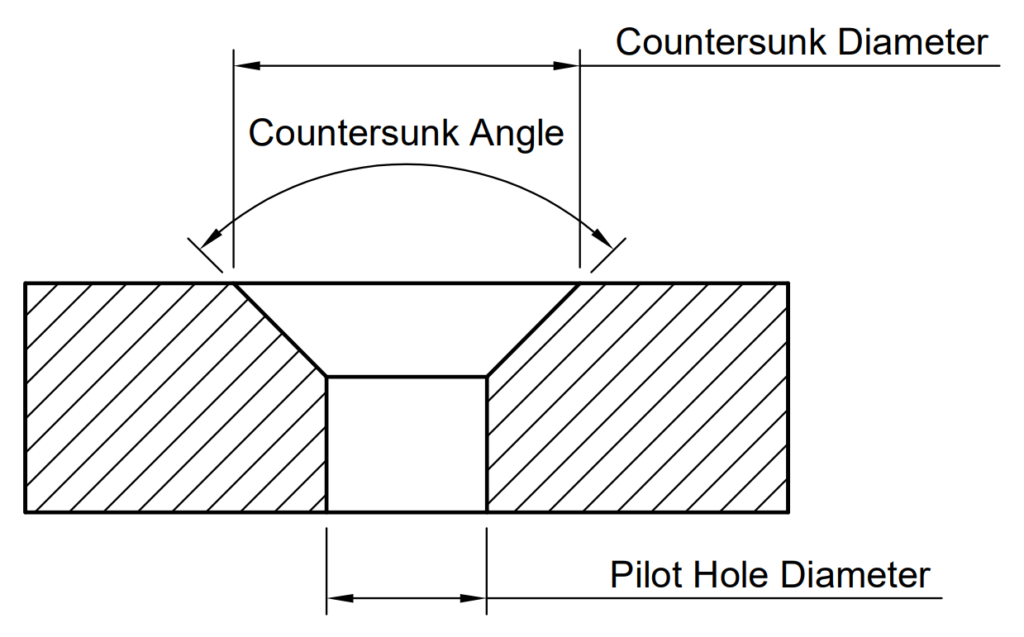
Countersunk Hole Size Chart for Machine Fasteners (ANSI Metric)
All dimensions are in millimetres apart from the countersink angle.
Fastener Size (Thread) | Pilot Hole Diameter (Close Fit H12) | Pilot Hole Diameter (Normal Fit H13) | Pilot Hole Diameter (Loose Fit H14) | Countersink Diameter | Countersink Angle |
| M2 | 2.2 | 2.4 | 2.6 | 4.4 | 90 |
| M2.5 | 2.7 | 2.9 | 3.1 | 5.5 | 90 |
| M3 | 3.2 | 3.4 | 3.6 | 6.3 | 90 |
| M3.5 | 3.7 | 3.9 | 4.2 | 8.2 | 90 |
| M4 | 4.3 | 4.5 | 4.8 | 9.4 | 90 |
| M5 | 5.3 | 5.5 | 5.8 | 10.4 | 90 |
| M6 | 6.4 | 6.6 | 7 | 12.6 | 90 |
| M8 | 8.4 | 9 | 10 | 17.3 | 90 |
| M10 | 10.5 | 11 | 12 | 20 | 90 |
If you want to learn more about countersunk holes, see our post here.

